How to Prompt Claude for Elite Outputs (Anthropic's Guide)

Anthropic recently released a masterclass on prompt engineering.
This internal framework is built to deliver top-tier AI responses, and if you use Claude regularly, you need to add this to your prompting toolkit.
Anthropic's optimal prompting structure follows 10 steps, but before I dive into the step-by-step process, we have to talk about model selection.
Model Selection Process - 4.5 Family
Opus 4.5 - Anthropic's smartest model. Best for complex reasoning, deep analysis, coding tasks, and tasks requiring genuine intelligence.
Sonnet 4.5 - Balanced workhorse. Strong reasoning with faster speed and lower cost than Opus. Best for most everyday tasks.
Claude Haiku 4.5 - The speed demon. Fastest and cheapest. Best for high-volume, straightforward tasks - I personally really like this option in the Claude Chrome extension.
Prompting Structure
Below is Anthropic's recommended prompting structure.

Let's break this down step by step with real examples.
Task Context
This is arguably the most essential part of any prompt.
Think of this as setting the role + task at hand.
Example:

2. Tone Context
This step defines the communication style with the LLM (e.g., professional, casual, warm).
The exact tone content you use will depend on the model you're prompting.
Example of combined Task + Tone Context:

3. Background Data
Background data is key in any prompt that requires a detailed answer.
Think: Uploading PDFs, Files, Context Profiles.
Example: Use this doc [insert doc] to execute the above Task + Tone context.
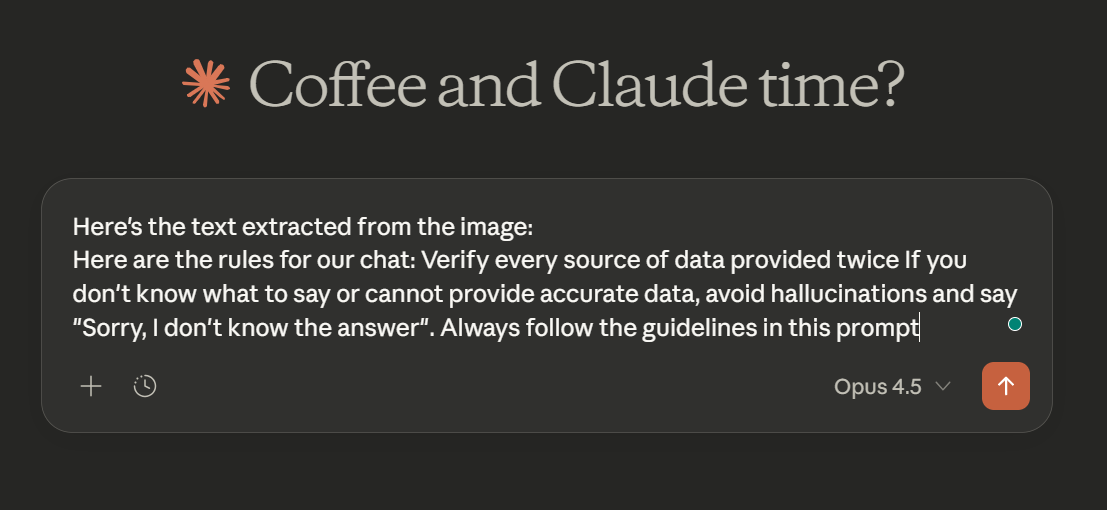
4. Detailed Task Description & Rules
Now it's time to expand on your task/goal with the proper constraints/guidelines.
Example:
5. Examples
My best LLM outputs have always included tangible examples to give the model.
If you've received a desired output and want the LLM to reference it, use this tag in your prompts: <example>
6. Conversation History
Most people don't know this, but you can actually tell most LLMs to reference conversation history (this is a good alternative if you don't have any examples of the desired outputs).
Just include this in your prompts:
"Call back on our previous conversations that have talked about this topic..."
Or use the tag <HISTORY> in your prompts to inject previous conversation history.
7. Immediate Task Description
This is the thing you want the AI to do right now.
It's different from the broader task context (step one) as it's the immediate action item.
Pro tip here: Use Verbs
Cheatsheet from Claude itself:

8. Deep Thinking
Enabling deep thinking is key to solving complex tasks.
It prompts the model to reason and greatly increases output accuracy.
In LLMs like Claude, inserting mini prompts such as "Think Deeply" triggers the model's deep reasoning capabilities.
With vs Without Thinking Prompting:

9. Output Formatting
Before sending your prompt,
recommends specifying the exact output format you want.
I often use bullet points (they're concise, quick), but feel free to use any of these output formats below:

10. Prefilled Response
Lastly,
recommends using a prefilled response (if any). A great way to organize data and the task at hand.
This isn't a necessity, more like icing on the cake for prompting structure.

Bringing it all together
So for optimal Claude responses, your prompts should include as many puzzle pieces as possible:
[Task Context] + [Tone Context] + [Background data] + [Detailed task description] + [Examples] + [Conversation history] + [Immediate action] + [Deep thinking] + [Output formatting] + [Prefilled respose]
Anthropic's complete diagram does a great job of putting all 10 pieces of the prompting structure together.
You can see the color-coded segment below:

While this process may seem long for writing prompts, it doesnt have to be.
I highly recommend automating this detailed prompt-building process.
One way is to vibe-code a prompt generator based on these principles.
You input a prompt, and the website/app/dashboard then turns it into a detailed prompt based on these 10 principles.
Another option is to create an LLM prompt generator project.
Just add this article as a context file, and whenever you send text to the project, the LLM will convert it into a detailed prompt.
Tools/Resources
In addition to the above prompting structure, the following prompting resources will help you get elite outputs.
Prompt Engineering Overview Docs by Anthropic
https:// platform.claude. com/docs/en/build-with-claude/prompt-engineering/overview
Anthropic's Interactive Prompt Engineering Guide
https://github.com/anthropics/prompt-eng-interactive-tutorial
Prompt Engineering PDF Guide by Anthropic
https:// www-cdn.anthropic. com/62df988c101af71291b06843b63d39bbd600bed8.pdf
Anthropic Prompt Library
https://platform.claude.com/docs/en/resources/prompt-library/library
Awesome Claude Prompts
https://github.com/langgptai/awesome-claude-prompts
Outro
If you made it this far, thank you for reading, and I hope you extracted value from this guide.
Subscribe to receive such guides daily in your inbox
Subscribe to Updates
Get notified when new posts are published.